Psoriasis Vulgaris
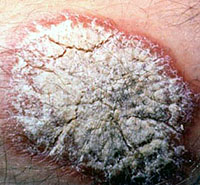 Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease of the skin characterized with increased epidermal proliferation. Usually the lesions are erythematous plaques covered by silver colored scales. Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease of the skin characterized with increased epidermal proliferation. Usually the lesions are erythematous plaques covered by silver colored scales.
It is a common skin disease and it usually involves knees, elbows, scalp, genital region and trunk.
The cause of psoriasis remains elusive. Both genetic factors and exogenous triggers predispose the disease.
Psoriasis is hereditary to some degree. Families with psoriasis can be found throughout the population. The gene responsible for psoriasis is found on the 6p chromosome near the HLA-C locus.
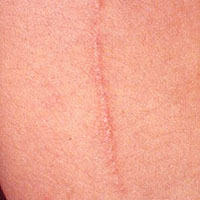 Trauma is an important triggering factor. It is usually thought that the onset of the disease is caused by a mechanical trauma. In some skin diseases trauma to normal skin may bring out the symptoms of the disease in a pattern that suits the pattern of the trauma. This is known as "Köbner phenomenon". These symptoms appear approximately 14 days after the trauma. It can be seen in psoriasis, lichen planus, verrucas and vitiligo. Trauma is an important triggering factor. It is usually thought that the onset of the disease is caused by a mechanical trauma. In some skin diseases trauma to normal skin may bring out the symptoms of the disease in a pattern that suits the pattern of the trauma. This is known as "Köbner phenomenon". These symptoms appear approximately 14 days after the trauma. It can be seen in psoriasis, lichen planus, verrucas and vitiligo.
Psoriasis can be triggered by infections, stress, pregnancy and delivery, hypocalcemia, drugs; especially beta-blockers, antimalarials, and lithium. Factors such as smoking, obesity, regional enteritis, HIV infection can influence the outcome of the disease.
| Epidermal Parameters in Psoriasis |
| |
Normal |
Psoriasis |
| Mitosis |
0.4% |
2.5% |
| DNA synthesis |
3-5% |
20-25% |
| Cell cycle |
457 hrs |
37 hrs |
| Epidermal transit time |
28 days |
3-4 days |
| Cell metabolism |
Normal |
Markedly increased |
| Stratum corneum |
Orthokeratotic |
Hyper- and parakeratotic |
|
 Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease of the skin characterized with increased epidermal proliferation. Usually the lesions are erythematous plaques covered by silver colored scales.
Psoriasis is an inflammatory disease of the skin characterized with increased epidermal proliferation. Usually the lesions are erythematous plaques covered by silver colored scales. Trauma is an important triggering factor. It is usually thought that the onset of the disease is caused by a mechanical trauma. In some skin diseases trauma to normal skin may bring out the symptoms of the disease in a pattern that suits the pattern of the trauma. This is known as "Köbner phenomenon". These symptoms appear approximately 14 days after the trauma. It can be seen in psoriasis, lichen planus, verrucas and vitiligo.
Trauma is an important triggering factor. It is usually thought that the onset of the disease is caused by a mechanical trauma. In some skin diseases trauma to normal skin may bring out the symptoms of the disease in a pattern that suits the pattern of the trauma. This is known as "Köbner phenomenon". These symptoms appear approximately 14 days after the trauma. It can be seen in psoriasis, lichen planus, verrucas and vitiligo.