HERPES SIMPLEXCausative agent of herpes simplex is Herpesvirus hominis (HSV) that involves both skin and nerves. Two antigenic types of this virus are type 1 and type 2. Type 1 and type 2 of HSV generally lead an infection above and below the waist, respectively. Contamination generally occurs in childhood ages. Virus inoculation is easy to disintegrated skin and mucous surfaces, but the friction of virus containing material can also infect intact skin and mucosa. Ninety-nine percent of the patients do not have any clinical symptoms and signs after contamination. Those patients are described as in "carrier stage". Nevertheless, 1% of the patients show clinical infection (Primary herpes simplex infection). After the improving of the primary infection, those patients are also a carrier. This means that virus will be found in infected person lifelong. Primary Herpes Simplex InfectionsPrimary herpes simplex infections have severe clinical symptoms and signs. Main subjective symptom of this group is pain. 1. Primary Herpetic GingivostomatitisPatients are mainly infants. Multiple vesicles appear in the mouth. After the burst of vesicles, erosions occur secondarily. These erosions have an appearance mimicking that whole oral mucosa is covered by multiple aphthae. Characteristically salivary secretion increase and there is a bad odor in mouth. Painful erosions lead also to feeding disturbances in infants. Additionally meningitis and encephalitis may be seen besides high fever, malaise and general complaints. 2. Primary Herpes GenitalisPatients are mainly adolescents. In this type primary herpes simplex entrance site of the HSV is genital area in the firstly contacting person with this virus. Painful grouped vesicles appear on the entrance area. Additionally meningitis and encephalitis may be seen besides high fever, malaise and general complaints. 3. Primary Herpetic KeratoconjunctivitisIf the first HSV inoculation occurs to eyes, this type herpes simplex is seen. One can initially see vesicles, then painful erosions after the bursting. 4. Primary Herpetic Whitlow
5. Disseminated Herpes Simplex Infection of NeonatesIf maternal genital area has HSV, viruses may contaminate the neonate during the delivery. Visceral organs are also involved beside skin and mucosa. This is the most severe primary herpes simplex type and may be fatal. According the accepted theory, virus shuttles periodically between entrance area and medulla spinalis in the 100% of the HSV infected persons. So, the virus periodically comes to entrance area and viral shedding occurs without clinical manifestation. Thus, the patient can contaminate other persons easily in this stage. Recurrent herpes simplex infections occur in the people exposed to predisposing factors during the viral shedding. Predisposing factors are mainly acute infections, stress, excessive exposing to ultraviolet radiation and menstruation. |
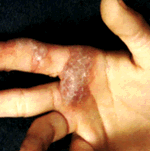 If the first HSV inoculation occurs to fingers, this type herpes simplex
is seen. One can grouped vesicles on the entrance area as in other herpes simplex
types. Spreading to palms leads to a honeycomb appearance of the vesicle group.
If the first HSV inoculation occurs to fingers, this type herpes simplex
is seen. One can grouped vesicles on the entrance area as in other herpes simplex
types. Spreading to palms leads to a honeycomb appearance of the vesicle group.